Huidige gevorderde BMI-weëe gaan verby eenvoudige gewigsmetings deur Bio-elektriese Impedansie-analise (BIA) met slim KI-tegnologie te kombineer om gebruikers werklike insig in hul liggaamsamestelling te gee. Die BIA-werk deur klein elektriese seine deur die liggaam te stuur, wat help om dinge soos spierinhoud, vetvlakke en selfs hoe gehidreerd iemand is, vas te stel. Slim algoritmes neem hierdie data en verfyn dit op grond van faktore soos ouderdom, geslag, fisiese aktiwiteitsgewoontes en veranderinge oor tyd. Dit maak die lesings baie akkurater, en verminder foute wat veroorsaak word deur tydelike waterretensieprobleme met ongeveer 40%. Wanneer dit teen mediese standaarde getoets word, meet hierdie toestelle tipies spiermassa binne ongeveer 3,5% akkuraatheid en skat interne vetvlakke binne slegs 0,8 punte verskil. So 'n presisie is nie net indrukwekkende syfers op 'n skerm nie – dit help werklik om potensiële gesondheidsprobleme vroegtydig op te spoor voordat hulle ernstige kwessies word.
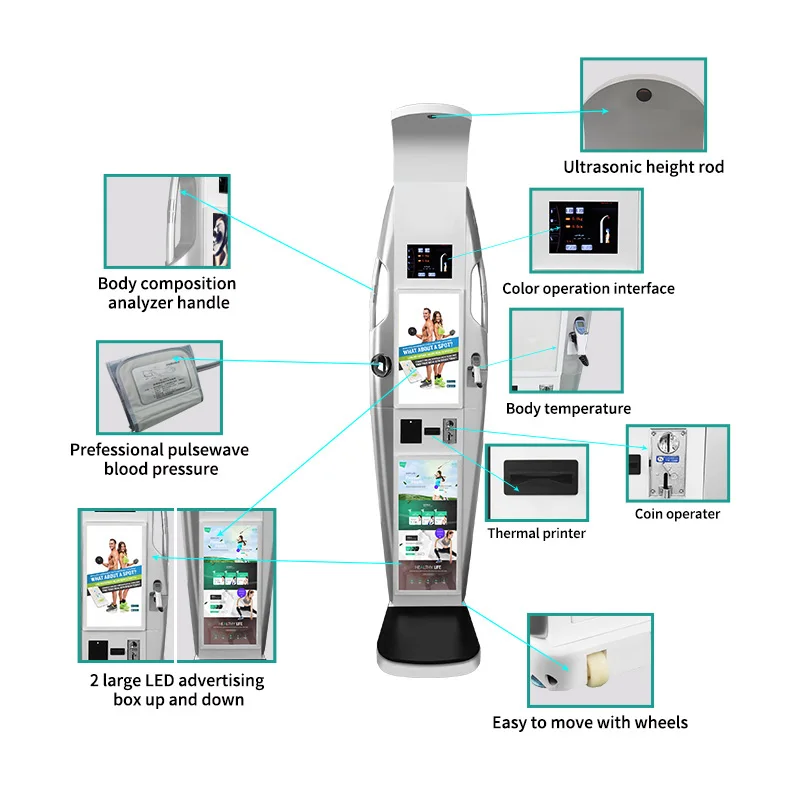
Toetsing teen gevestigde metodes soos Dual-Energy X-straal Absorptiometrie (DEXA) skande en MRI-beeldvorming toon dat top slim BMI-skaale lewer betroubare resultate in kliniese instellings. Navorsingsartikels het ook redelik sterk korrelasies gevind, ongeveer 0,92 by die meting van algemene liggaamsvet en ongeveer 0,89 spesifiek vir buikvet. Wat laat hierdie toestelle so goed werk? Hulle kombineer multi-frekwensie bioelektriese impedansie-analise (BIA) sensore met slim algoritmes wat aanpas vir alledaagse faktore wat ons dikwels oorsien. Dink aan hoe iemand op die weegskaal staan, waar hul voete geplaas is, selfs veranderinge in vertrektemperatuur gedurende die dag. Hierdie aanpassings maak baie verskil in werklike situasies. Dokters voel tans gemaklik met die gebruik van lesings van hierdie verbruikertoestelle as deel van hul gewone kontroles, veral wanneer hulle pasiënte met gewig-verwante gesondheidskwessies monitor of opvolg na lewensstylintervensies om te sien of behandellings werklik 'n verskil maak.
Data van slim weegskaale wat lengte, gewig en BMI meet, beweeg veilig na digitale gesondheidstelsels deur gebruik te maak van iets genaamd FHIR-kompatibele API's. Hierdie standaardverbindings laat inligting onmiddellik sinchroniseer met dinge soos elektroniese gesondheidsrekords van Epic MyChart, sowel as gewilde applikasies soos Apple Health en Google Fit. Wanneer mense nie meer hul getalle met die hand hoef in te tik nie, bly die data akkuraat oor tyd. Ons kan veranderinge in BMI-metings, spierkomposisie, en selfs vlakke van interne buikvet wat dokters noukeurig monitor vir toestande soos hoë bloeddruk, diabetesprobleme, en hartkwesties, dop hou. Dokters sien dadelik wat pasiënte rapporteer, in plaas daarvan om te wag vir papiervorms of deur ingewikkelde tussenliggende sagtewarelae te werk net om basiese metings te kry.
Wanneer dit by data-uitruil kom, word HIPAA se Sekerheidsreël gevolg deur OAuth 2.0 token-gebaseerde verifikasie. Hierdie stelsel toets wie 'n persoon werklik is en verseker dat hulle spesifieke toestemming gee voordat hulle toegang tot Beskermde Gesondheidsinligting kry. Die proses werk so: pasiënte kan presies kies watter inligting verskillende programme kan sien. Byvoorbeeld, mag hulle 'n program toelaat om BMI-metings te sien, maar toegang tot dinge soos viscerale vetmetings blokkeer. Op dié manier stem hul privaatheidinstellings ooreen met wat die regulasies vereis. Statische aanmeldbesonderhede word nie hier gebruik nie omdat hulle te lank bly. In plaas daarvan skep OAuth tydelike tokens wat na 'n rukkie verdwyn, wat beteken dat daar minder risiko is indien hulle per ongeluk afgeluister word. Vanuit 'n praktiese oogpunt maak hierdie metode werklik lewe makliker vir almal betrokke. Wanneer mens kyk na gesondheidsorg-gebruikerservaringsstatistieke wat verlede jaar vrygestel is, spandeer dokters en pasiënte ongeveer 62% minder tyd om hierdie stelsels op te stel in vergelyking met ouer verifikasiemetodes. Ons kry dus gelyktydig beter sekuriteit en vlotter operasies.
Kry mense om werklik toestelle te gebruik, hang baie af van hoe maklik dit is om dit op te begin, en daar is stewige navorsing wat dit ondersteun. Indien Bluetooth langer as ongeveer 90 sekondes neem om koppel, gee ongeveer 'n derde van mense heeltemal op, volgens 'n studie van Clinical UX in 2023. Slim weegskaale wat lengte, gewig en BMI meet, het maniere gevind om hierdie probleem te omseil deur hul koppelprotokolle aan te pas. Hierdie toestelle behou steeds sterk sekuriteitsnorme wat voldoen aan NIST-vereistes, maar verwyder onnodige verifikasie-stappe wat die proses vertraag. Party slim tegnieke wat hierdie weegskaale gebruik, sluit in die uitsending van seine selfs voordat dit heeltemal aangeskakel is, die apart hou van spesifieke bandwydte net vir die uitruil van aanmeldinlig, en die outomatiese oorskakeling na Bluetooth Low Energy-modus wanneer radio-ontstigting die verbinding beïnvloed. Al hierdie aanpassings help om te verseker dat die meeste mense hul skaal binne 90 sekondes kan koppel, ongeag die tipe draadlose omgewing waarin hulle tuis is.
Hierdie weëe voer bio-elektriese impedansie-analise plaaslik uit deur gebruik te maak van ingeboude mikroprosessor — rou elektriese seine word omgeskakel na gevalideerde liggaamsamestellingmetrieke voordat enige data die toestel verlaat. Slegs geïnterpreteerde uitvoere — nie rou biometriese strome nie — word oorgedra via versleutelde TLS 1.3-verbindinge. Hierdie randrekenargitektuur bied drie kernvoordele:
| Sekuriteitsvoordeel | Tegniese Implementering |
|---|---|
| Data-minimalisering | PHI beweeg nooit oor netwerke nie; slegs delta-waardes word gesinkroniseer via TLS 1.3 |
| Vermindering van Aanvalsoppervlak | 68% minder PHI-aanrakingspunte in vergelyking met rou-seintjeargitektuure |
| Regulering nakoming | Ingeboude veiligheidsmaatreëls wat strook met HIPAA §164.312(e)(1) |
Krities, behou hierdie ontwerp 98,2% kliniese akkuraatheid relatief tot DEXA — wat bewys dat privaatheidbehoudende berekening nie hoef in te boet op diagnostiese bruikbaarheid nie.


Kopiereg © 2025 deur Shenzhen Sonka Medical Technology Co., Limited - Privaatheidsbeleid